Jadi.....ortodontik, sebelumnya ortodonsi (dari Orthos
Yunani "lurus atau tepat atau
sempurna", dan odous "gigi") adalah khusus pertama kedokteran gigi yang berkaitan dengan studi dan perawatan maloklusi (gigitan yang
tidak benar), yang mungkin akibat dari gigi ketidakteraturan, hubungan rahang yang tidak proporsional, atau keduanya. Perawatan ortodontik dapat fokus pada perpindahan gigi saja, atau dapat
menangani kontrol dan modifikasi
pertumbuhan wajah. Dalam kasus terakhir itu lebih baik didefinisikan sebagai "ortopedi
Dentofacial". Perawatan ortodontik
dapat dilakukan semata karena alasan
estetika berkaitan dengan meningkatkan penampilan umum dari gigi pasien. Namun, ada
ortodontis yang bekerja untuk merekonstruksi seluruh wajah daripada berfokus secara eksklusif pada
gigi.
This,is
Orthodontics is a branch of dentistry that specializes in treating patients with improper positioning of teeth when the mouth is closed (malocclusion), which results in an improper bite. Orthodontics also includes treating and controlling various aspects of facial growth (dentofacial orthopedics) and the shape and development of the jaw. An orthodontics specialist is called an orthodontist.
Orthodontics used to be called orthodontia - the word comes from the Greek orthos, meaning "straight, perfect or proper", and dontos, which means "teeth".
Orthodontics also includes cosmetic dentistry; when the patient's aim is to improve his/her appearance.
An orthodontist uses a range of medical dental devices, including headgears, plates, braces, etc. to help in:
Thumb sucking (or finger sucking) can result in localized deformation of the teeth and supporting bone. In order to restore a natural improvement, the thumb sucking habit has to be stopped.
Generally, malocclusions do not affect physical health, malocclusion is not a disease, it is a variation in the normal position of teeth. However, it may impact on the shape of the person's face and the appearance of their teeth, which can lead to embarrassment, a lack of self-confidence, and even depression
Severe malocclusion may affect eating, speech and keeping the teeth clean.
UK health authorities say that approximately one third of all 12 year-olds in the country probably need orthodontic treatment. People may require orthodontic treatment for different problems:
Children with a cleft lip and palate may require orthodontic treatment before their adult teeth have developed completely.
Good oral hygiene is essential before any orthodontic work can begin. When devices are placed on the teeth, bits of food are much more likely to become stuck; the patient will need to brush much more carefully and more often to prevent tooth decay while treatment is ongoing.
Patients who have not reached good oral hygiene standards beforehand are much more likely to suffer from tooth decay after treatment begins.
Fixed appliances - the most common devices used in orthodontics. They are used when precision is important. Although the patient can eat normally with fixed appliances, some foods and drinks need to be avoided, such as carbonated drinks, hard sweets, or toffee. People who participate in contact sports need to tell their orthodontist, so that special gum shields can be made.
Examples of fixed appliances include:
Examples of removable appliances include:
Orthodontics is a branch of dentistry that specializes in treating patients with improper positioning of teeth when the mouth is closed (malocclusion), which results in an improper bite. Orthodontics also includes treating and controlling various aspects of facial growth (dentofacial orthopedics) and the shape and development of the jaw. An orthodontics specialist is called an orthodontist.
Orthodontics used to be called orthodontia - the word comes from the Greek orthos, meaning "straight, perfect or proper", and dontos, which means "teeth".
Orthodontics also includes cosmetic dentistry; when the patient's aim is to improve his/her appearance.
An orthodontist uses a range of medical dental devices, including headgears, plates, braces, etc. to help in:
- Closing wide gaps between the teeth
- Making sure the tips of the teeth are aligned
- Straightening crooked teeth
- To improve speech or eating (oral function)
- To improve the long-term health of gums and teeth
- To prevent long-term excessive wear or trauma (of the teeth)
- Treating an improper bite
What is malocclusion?
Malocclusion literally means bad bite. Some children's jaws and teeth do not develop properly. Malocclusion refers to crooked, misaligned teeth and a fault in the relation between the bottom and top set of teeth (the two dental arches). This may develop because of injury to the teeth or facial bones, frequent thumb sucking, or for reasons unknown.Thumb sucking (or finger sucking) can result in localized deformation of the teeth and supporting bone. In order to restore a natural improvement, the thumb sucking habit has to be stopped.
Generally, malocclusions do not affect physical health, malocclusion is not a disease, it is a variation in the normal position of teeth. However, it may impact on the shape of the person's face and the appearance of their teeth, which can lead to embarrassment, a lack of self-confidence, and even depression
Severe malocclusion may affect eating, speech and keeping the teeth clean.
UK health authorities say that approximately one third of all 12 year-olds in the country probably need orthodontic treatment. People may require orthodontic treatment for different problems:
- The front teeth protrude - treatment not only improves the patient's appearance, but also protects the teeth from damage; people with protruding front teeth are more likely to injure them in sports, falling down, etc.
- Crowding - if the patient's jaw is narrow, there may not be enough space for all the teeth. In such cases the orthodontist may have to remove one or more teeth to make room for the others.
- Impacted teeth - as the adult teeth come through, they are not in the right position
- Asymmetrical teeth - the upper and lower teeth do not match, especially when the mouth is closed but the teeth are showing.
- Deep bite (overbite) - when the teeth are clenched, the upper ones come down over the lower ones too much
- Reverse bite - when the teeth are clenched, the upper teeth bite inside the lower ones
- Open bite - when the teeth are clenched, there is an opening between the upper and lower teeth.
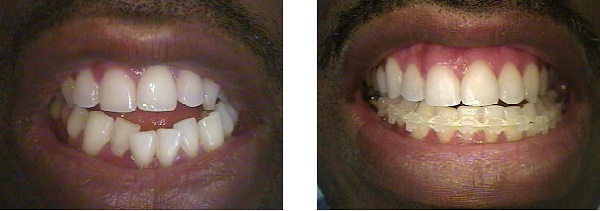
Example of open bite, before and after treatment - Underbite - the upper teeth are too far back, or the lower teeth a too far forward ("bulldog" appearance)
- Crossbite - at least one of the upper teeth does not come down slightly in from of the lower teeth when the teeth are clenched; they are too near the cheek or the tongue
- Spacing - there are gaps or spaces between the teeth, either because a tooth is missing, or the teeth simply do not fill-up the mouth (opposite of crowding)
When can orthodontic treatment start?
Treatment will not usually commence until the child is about 12 or 13 years old; when the adult teeth have come through and developed fully. In some cases treatment may start a couple of years later if teeth problems had not become noticeable beforehand.Children with a cleft lip and palate may require orthodontic treatment before their adult teeth have developed completely.
Good oral hygiene is essential before any orthodontic work can begin. When devices are placed on the teeth, bits of food are much more likely to become stuck; the patient will need to brush much more carefully and more often to prevent tooth decay while treatment is ongoing.
Patients who have not reached good oral hygiene standards beforehand are much more likely to suffer from tooth decay after treatment begins.
Diagnosing dental problems and recommending treatment options
Assessment - the orthodontist will assess the state of the patient's teeth and make a prediction on how they are likely to develop without treatment. The following diagnostic procedures will be performed:- A full medical and dental health history
- A clinical examination
- X-rays of the teeth and jaw
- Plaster models of the teeth
Examples of orthodontic appliances
There are two types of orthodontic appliances: fixed and removable ones.Fixed appliances - the most common devices used in orthodontics. They are used when precision is important. Although the patient can eat normally with fixed appliances, some foods and drinks need to be avoided, such as carbonated drinks, hard sweets, or toffee. People who participate in contact sports need to tell their orthodontist, so that special gum shields can be made.
Examples of fixed appliances include:
- Braces - consisting of brackets and/or wires and bands. Bands
are fixed firmly around the teeth and serve as anchors for the
appliance, while brackets are usually connected to the front of the
teeth.
Wires in the shape of an arch pass through the brackets and are fixed to the bands. As the arch wire is tightened, tension is applied to the teeth, which over time moves them into proper position.
A patient sees the orthodontist once a month so that the braces can be adjusted. The treatment course may last from several months to a number of years.
Children tend to prefer the colored braces, while adults usually go for the clear styles.
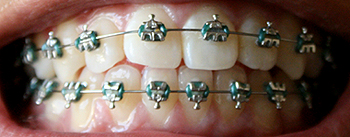 Dental braces
Dental braces - Fixed space maintainers - if the child loses a milk tooth, a space maintainer will stop the two teeth at either side of the spaces from moving into it until the adult tooth comes through. A band is fixed to one of the teeth next to the space, and a wire goes from the band to the other tooth.
- Special fixed appliances - these may be recommended to control tongue thrusting or thumb sucking. Patients may find them uncomfortable, especially when they are eating. Experts say they should only be used if they are really necessary .
Examples of removable appliances include:
- Aligners - an option instead of traditional braces for adult patients. They are virtually unnoticeable by other people and can be taken out when patients brush their teeth, floss, or eat.
- Headgear - there is a strap around the back of the head, which is attached to a metal wire in the front, or face bow. The aim is to slow down upper jaw growth, and keeping the back teeth in position while the front ones are pulled back.
- Lip and cheek bumpers - specially made to relieve the pressure of cheeks or lips on the teeth.
- Palatal expander - an appliance designed to make the arch of the upper jaw wider. The device consists of a plastic plate that is placed in the palate (the roof of the mouth). The plate has screws which exert pressure on the joints in the bones, forcing them outward, thus expanding the size of the palatal area (roof of mouth area).
- Removable retainers - these are placed on the roof of the mouth. They are designed to stop the teeth from moving back to their original positions. If modified, they may also be used to stop children from sucking their thumbs.
- Removable space maintainers - an alternative to fixed space maintainers.
- Splints (jaw repositioning appliances) - they are placed either in the top or lower jaw and help the jaw close properly. Splints are commonly used for TMJ (temporomandibular joint disorder) syndrome.